Probability
Lecture 10
Dr. Elijah Meyer
Duke University
STA 199 - Spring 2023
February 15th, 2023
Checklist
– Exam-1 is over! Congratulations on your hard work
– Clone ae-09
– HW-2 coming FRIDAY
Feedback
– HW’s, labs, AE’s and exam; there are a lot of submissions to keep track of
– I wish there was a cheat sheet for all the appropriate formatting for our HWs and labs.
– Structure of ae’s (i.e. consistently not finishing ae material in class)
– I think that sometimes it would be helpful to do a quick review in the lecture of what we’ve learned the class before.
Where we are going
\(\checkmark\) Data Viz
– Probability
– Modeling Data
Goals
have a working understanding of the terms probability, sample space, event, population and sample.
compute probabilities of events from data
create a contingency table using pivot_wider() and kable()
use a contingency table to explore the relationship between two categorical variables.
Probability
– The probability of an event tells us how likely an event is to occur
takes on values from 0 to 1
the proportion of times the event would occur if it could be observed an infinite number of times
our degree of belief an event will happen
An Event
– is the basic element to which probability is applied, e.g. the result of an observation or experiment
Example: A is the event a student in STA 199 is a sophomore
We use capital letters, e.g. A to denote events
The oppositve of the Event
– If A is the event a student in STA199 is a sophomore, what is the opposite?
For any event A and its complement is \(A^c\)
Can think about c as “not”
Pr(A) + Pr(\(A^c\)) = 1
Sample Space
– A sample space is the set of all possible outcomes
- Each outcome in the sample space is disjoint or mutually exclusive meaning they can’t occur simultaneously
Sample Space
– The sample space for year in school is….?
{Freshman, Sophmore, Junior, Senior}
each item brackets is a distinct outcome
The probability of the entire sample space is 1
Example
Suppose you are interested in the probability of landing on heads.
Define the following:
Event (and compliment)
Sample space

ae-09
More Complicated Probabilities
– And
– Or
– Conditional
Conditional Probabilities
– “Given an event has already happened…..”
– A | B
– Cuts up our contingency table
Work through
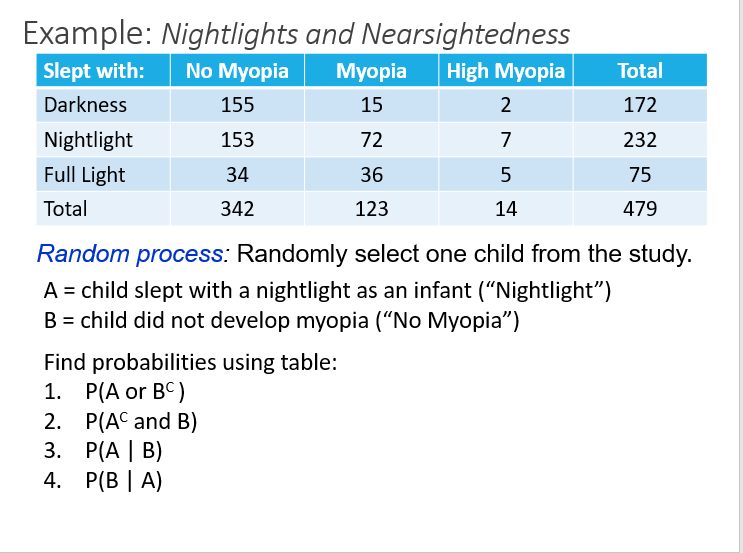
Work through
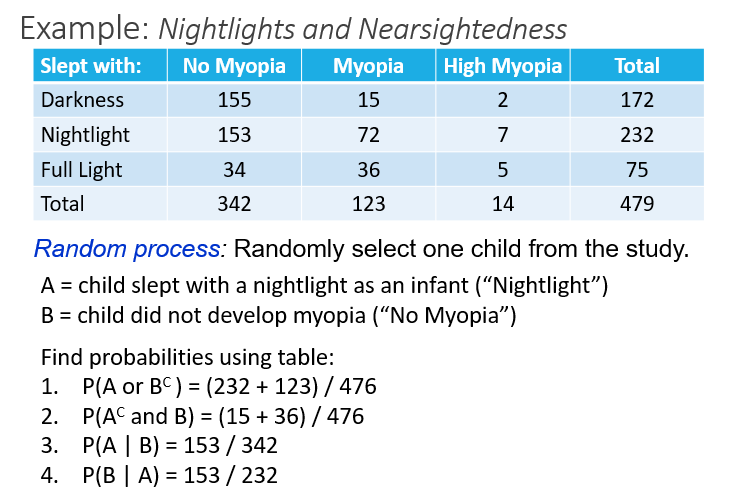
In Summary
– What is probability
– Event
– Sample Space
– Calculate probabilities in R
– And / Or / Conditional Probabilities
